The RSA cryptography platform is now 40 years old. While it has served well in the Internet and digital communications, Moore's law and the emergence of quantum computing. RSA and other forms of encryption. The rise of quantum computing makes cracking RSA and various other forms of encryption feasible in the near future. Classical computers use binary bits, which have a value of either zero or one. Strings of these zeroes and ones translate into data, but the nature of the bit means one calculation can be done at a time. However, with quantum computing, each quantum bit (called a qubit) can both be a zero and one at the same time. This difference means quantum computers can store vastly more data, and do many more calculations per second, making them perfect for code breaking applications.
With these quantum computing technologies, the time to act is now. Once RSA is cracked, mission critical applications like HTTPS, credit and debit card processing, and government systems face the immediate risk of compromise. The chaos resulting from such a hack would be totally disruptive to the social and economic framework of daily life.
This is why we are developing a quantum generated, secured data transmission platform called Quantum1Net. Leveraging quantum computing, we are able to provide a level of complexity in cryptographic key generation that is not possible by traditional means. We expect quantum computing to play a key role in the future of encryption.




This is why we are developing a quantum generated, secured data transmission platform called Quantum1Net. Leveraging quantum computing, we are able to provide a level of complexity in cryptographic key generation that is not possible by traditional means. We expect quantum computing to play a key role in the future of encryption.
Quantum1Net Prototype
The laboratory prototype of Quantum1Net's Quantum Random Number Generator, which has been developed in 2014, is based on a one-qbit optical device, that uses four photon detectors and time-to-digital (TDC) converters to generate sets of perfect random numbers with timestamps.
The quantum device consists of an entangled photons source, and linear optical
elements, which sets the quantum system to the desired state. Two configurations have been developed to generate sets of 4 and 6 elements respectively. The output of the TDC is the temporary queue, from which sets of unique random numbers or encryption keys can be requested, creating a real time, on demand encryption and decryption system.

TIMELINE ICO

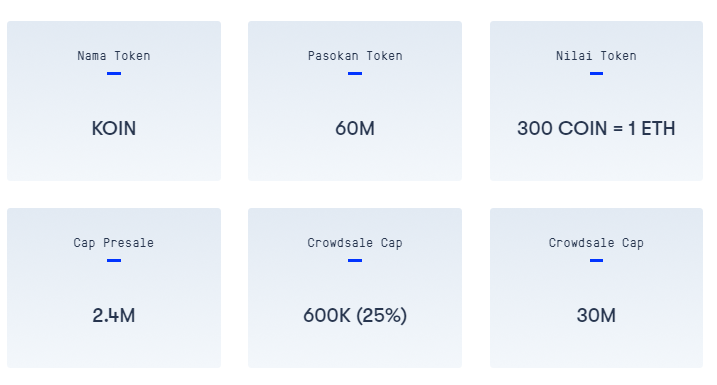
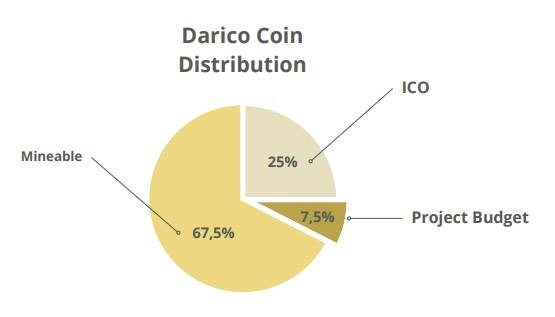
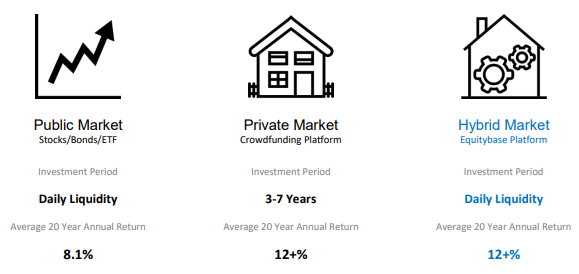
TOKEN


frequently asked questions are:
- Encryption methods seem to work very well. What is the problem?
- Why is quantum computing a threat to current encryption methods?
- Why is Bitcoin and other cryptococcal forms at risk because of quantum computing?
- How does quantum mechanics and quantum computing make the digital world safe again?
- What is superposition?
- What is entanglement?
- What is the difference between ordinary bit and qubit?
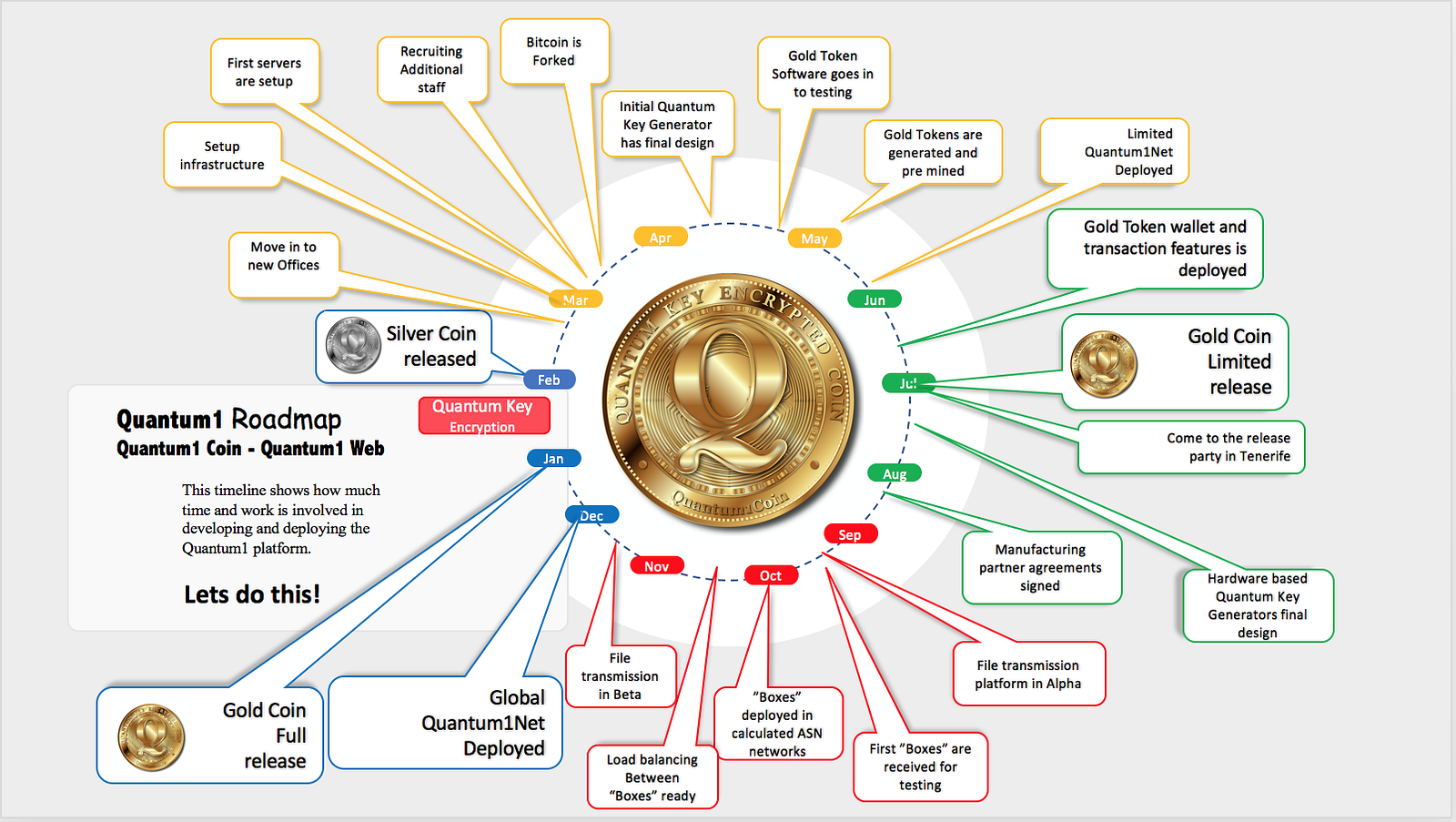
Quantum1Net Roadmap

for information :
website :https://quantum1net.com/
whitepaper :https://quantum1net.com/Q1N%20white%20paper.pdf
yellow paper :https://quantum1net.com/Q1N%20yellow%20paper.pdf
facebook :https://www.facebook.com/quantum1net
twitter :https://twitter.com/quantum1net
telegram :https://t.me/Quantum1Net
medium :https://medium.com/quantum1net
Author: Alex789
Bitcointalk profile: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=1653045
ETH: 0x5f5f506A001A179b8eE67214a7754Bfe04ffadE0